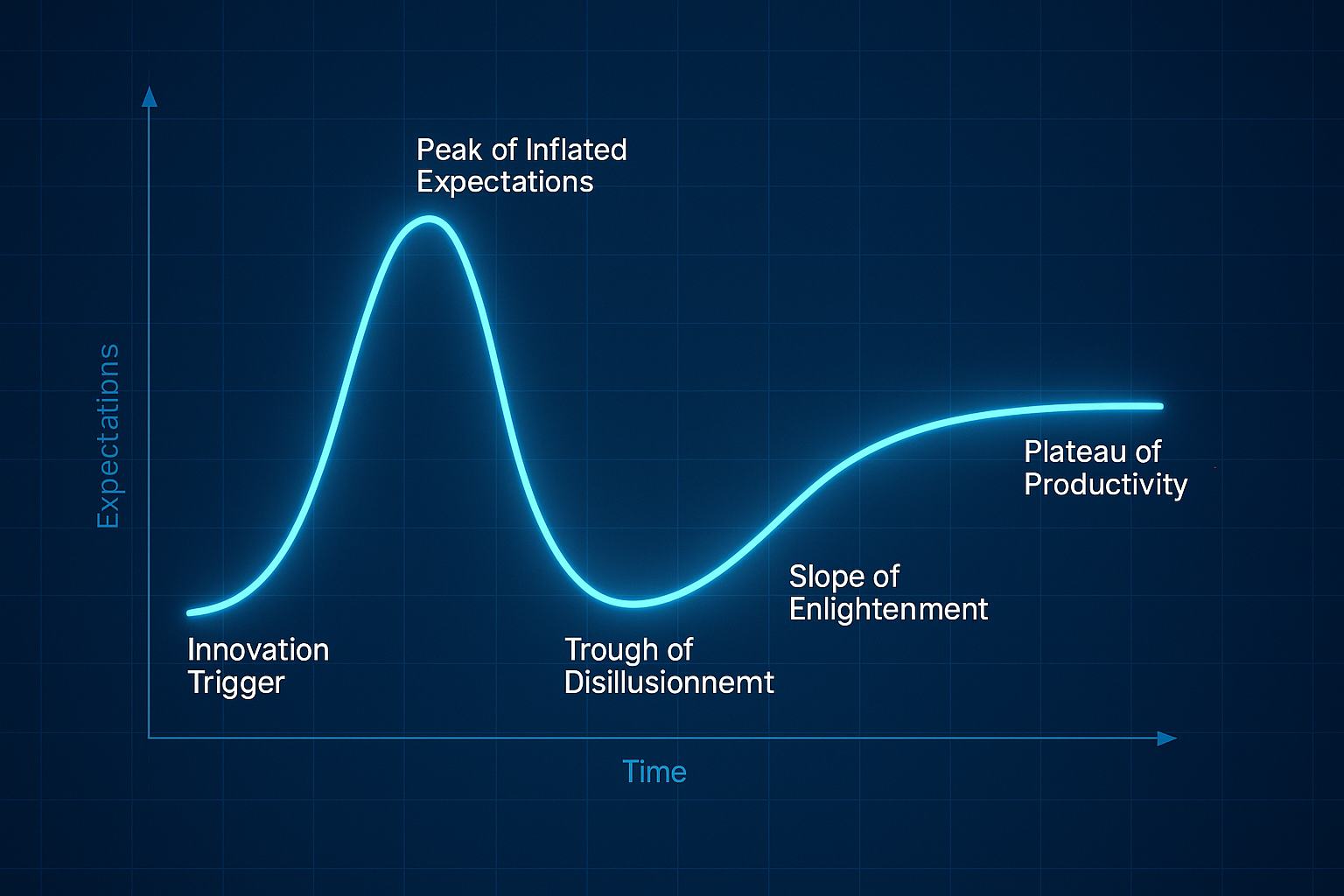
Risk modeling is essential to cybersecurity because it enables security practitioners to identify potential threats and control gaps, prioritize resources and investments, and develop strategies to manage and mitigate risks. By identifying potential threats and gaps in the existing cyber risk measures, leaders can take proactive steps to prevent or minimize the impact of an attack in real time.
By quantifying cyber risks, organizations can assess the likelihood of a cyberattack and its potential impact on their operations, finances, reputation, and customers. Risk modeling provides a framework for continuously improving and monitoring an organization's cybersecurity posture. By regularly reassessing risks and adapting their security strategies, organizations can stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain their resilience in the face of cyber attacks.
Regular cyber risk assessments and progress tracking are essential to communicate to business-side leaders and Board members as they show the progress made and what may need more attention. While there are many cyber risk quantification models, the FAIR model is a gold-standard approach that provides usefulness to security teams, CISOs, and the Board.
What is the FAIR Model?
FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) is a framework for quantifying and managing information risk. It is a quantitative risk analysis methodology that helps organizations understand and evaluate their information security risks in a structured and consistent manner.
The FAIR model is central to cyber risk quantification and involves assessing the probability and impact of potential information security events, such as data breaches or cyber-attacks, and then using this information to assign a dollar value to the risk. By quantifying the risk in this way, organizations can make more informed decisions about allocating resources to manage the risk.
Assigning a dollar value to cyber risk is crucial to its usefulness, as it standardizes how CISOs can communicate risk to Board leaders. It translates risk into more accessible terminology.
The FAIR framework consists of six steps:
| Steps | Actions |
| Scope of the Analysis | Determine what assets and threats are in range for the analysis |
| Identify Threats | Identify the potential events that could cause harm to the organization's assets |
| Identify Assets | Identify the organization's assets that the identified threats could impact |
| Evaluate Loss Event Frequency | Determine how frequently the identified threats could occur and affect the organization's assets |
| Evaluate Loss Magnitude | Determine the potential impact of the identified threats on the organization's assets |
| Calculate Risk | Use the information gathered in steps 4 and 5 to calculate the risk of each identified threat |
Drive Data-Backed Decision-Making with FAIR-based Risk Assessments
The FAIR framework provides a standardized methodology for quantifying and managing information security risks, helping organizations make more informed decisions about allocating resources to address them. By understanding the potential financial impact of different security events and their likelihood of occurring, CISOs and security leaders can strategize with business-side leaders and align cyber risk management operations with business operations.
Recognize the criticality of cyber risk to business success and establish a comprehensive FAIR-based cyber risk analysis approach. To learn more about the risk models offered through the CyberStrong platform, schedule a conversation.





.png)
.png)
.png)
%201.png)
.png)