Let’s begin with the complete title of what’s referred to as ISO 27001. It is officially known as “ISO/IEC 27001.” The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) collaborates with ISO to develop the ISO/IEC 27000 series, ensuring the standards are robust and widely applicable. If you’re looking to have your company certified, you’ll need to meet ISO 27001 criteria. The ISO 27000 standards include ISO 27002, ISO 27005, and ISO 27001; it has an extensive reference library of associated guidance materials.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developed this Information Security Management standard in 2005. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) also plays a key role as a governing body in developing and regulating these standards. It ensures organizations successfully manage data security concerns and helps them establish and sustain an effective information security management system (ISMS) through continuous improvement. You’ll need to quickly identify information security risks and implement procedures and policies to handle them during certification.
Is ISO 27001 compliance new to you? Do you want additional information about the information security standard? The ISO 27001 framework has grown in popularity amid rising public concern about data security breaches. ISO 27001 is part of a set of international standards recognized worldwide for information security best practices, providing organizations with a credible, universally accepted benchmark. Keep reading below to learn more about ISO and how to attain an ISO 27001 security certification.
Is ISO 27001 compliance new to you? Do you want additional information about the information security standard? ISO 27001 certification has grown in popularity amid rising public concern about data security breaches. Keep reading below to learn more about ISO and how to attain an ISO 27001 security certification.
Introduction to ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard that sets out the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This standard provides organizations with a systematic approach to managing sensitive data, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. By adopting a risk-based approach, ISO 27001 helps organizations identify and assess information security risks and implement appropriate controls to mitigate security risks. Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a commitment to robust information security management and can significantly enhance an organization’s reputation, building trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. As a leading international standard, ISO 27001 supports organizations in protecting sensitive data and aligning their management system with global security best practices.
Differences Between ISO 27001 and NIST CSF
The differences between ISO 27001 and NIST CSF are significant. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides federal agencies and enterprises guidance to manage risk better.
If applicable, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a technique for self-certification, namely “Certificate of Analysis and a Material Safety Data Sheet,” with every SRM. Your product will be tested against NIST SRM (standard reference materials) to qualify for NIST certification.
ISO 27001, on the other hand, is a method for developing and maintaining an ISMS that has gained international recognition. Audits and certification bodies are required to meet the requirements of ISO 27001, while the NIST CSF is optional. A certification body is an authorized third-party organization responsible for auditing and issuing ISO 27001 certificates to organizations that demonstrate compliance with the standard. Certification bodies themselves are accredited and regularly audited by an accreditation body to ensure they meet international standards.
Various control catalogs and five functions allow NIST frameworks to tailor cybersecurity controls to the organization’s needs. Alternatively, ISO 27001 emphasizes risk-based management and provides best practices to keep information secure. The ISO 27001 standard comprises 14 control categories, 114 controls, and ten management clauses in Annex A.
Operationally mature firms might consider the ISO 27001 certification. NIST CSF is best suited for firms in the early phases of building a cybersecurity risk policy or attempting to minimize breaches.
Information Security
Information security encompasses the strategies, policies, and procedures organizations use to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access, misuse, or loss. Effective information security management is essential for preventing data breaches and ensuring business continuity. ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive framework for managing information security risks, starting with a thorough risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. The standard emphasizes the importance of implementing access control measures, maintaining strong network security, and establishing clear incident response protocols to protect sensitive data. By following ISO 27001, organizations can proactively manage information security risks, adapt to evolving threats, and foster a culture of continuous improvement in managing information security.
Effectiveness of ISO 27001
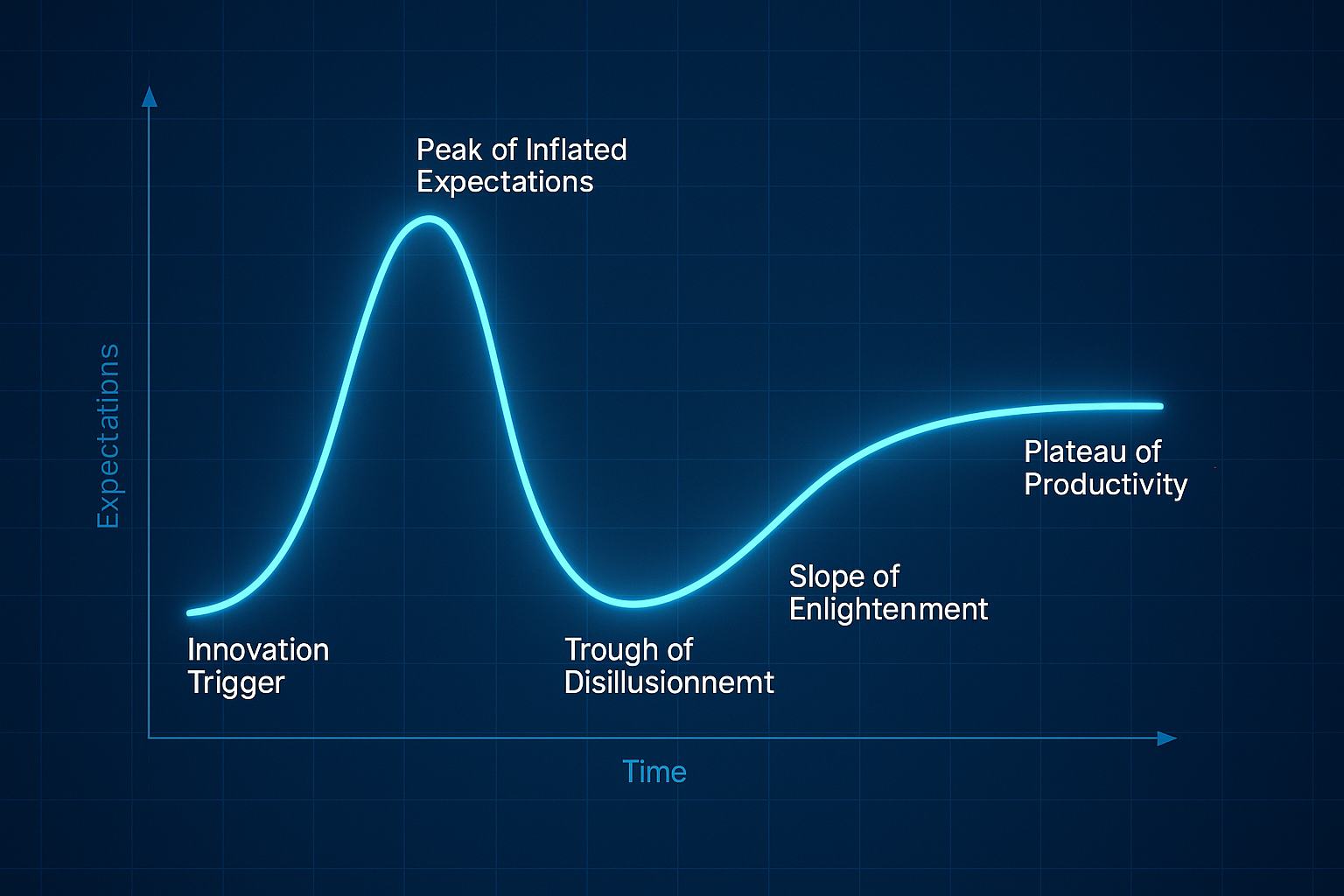
ISO 27001 prevents and reduces real-world information security incidents. When a framework has been adopted and certified, it aims to identify its practice areas, leading to high stakeholder certainty. It also focuses on loopholes contributing to information security risks and incidents, even when the framework is followed and certified.
Companies with ISO 27001 certification and audits benefit from a better risk-based approach to cybersecurity management, focusing on proactive countermeasures and increasing their security through extensive ISO testing. Performance evaluation, through internal audits and management reviews, is essential to assess the effectiveness of the Information Security Management System (ISMS) and ensure ongoing compliance. Organizations can use one system instead of two to demonstrate effective internal control over financial operations and improve information security concerns.
Continual improvement is a core principle of ISO 27001, ensuring the ISMS remains effective and up-to-date.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Being ISO 27001 Certified?
The only disadvantage of obtaining ISO 27001 framework certification is the additional cost of the extra work. On the other hand, it has numerous advantages for your company. The following are some benefits your company will receive:
-
Ensured organizational safety by closing any security gaps.
-
Decreased volume of cyberattacks.
-
Streamlined compliance with regulations
-
Helps organizations meet their compliance obligations by aligning with regulatory and industry requirements.
-
Can help attract enterprise customers who require high security and compliance standards from their vendors.
-
A significant advantage over competitors
-
New opportunities.
-
Reputation protection
-
Decreased frequency of audit requirements
-
Help with retaining customers
-
Quality assurance
Step-By-Step Process Plan of the ISO 27001
You must pass audits to be certified for ISO 27001. The official certification audit is a formal, third-party review required to achieve ISO 27001 certification. Here’s how to prepare and pass the exam to get an ISO 27001 certification.
Step One: Prepare a Project Plan
Check who oversees the process, sets expectations, and manages milestones. Distinguish how you will convince company leaders and whether you will seek an ISO 27001 consultant to help. Ensure the ISMS project plan aligns with the organization's strategic objectives to gain leadership support and ensure proper resource allocation.
A significant part of this procedure is learning the 114 controls of ISO 27001.
Step Two: Determine The Scope of Your Information Security Management System (ISMS)
Every company is different and has its respective statistics. Your ISMS will need to safeguard specific types of data, which you will need to identify beforehand.
While particular ISMSs cover the whole business, others are limited to a single department or system. Your team must decide what to include in the ISO 27001 scope statement. The scope should cover all relevant organizational processes that impact information security to ensure comprehensive protection and compliance.
Begin by questioning yourself: “Which service, product, or platform are our clients most interested in for ISO 27001?”
Step Three: Analyze Risks and Gaps
ISO 27001 certification requires a formal risk assessment. Make sure to document every step of your risk assessment. It is important to systematically assess risks to identify threats and vulnerabilities that could impact your organization. Regular risk assessments are essential for ongoing compliance and security. Start with your security baseline. What legal, regulatory, and contractual duties does your firm have? The risk assessment results will inform the development of the Statement of Applicability and help prioritize security measures. An ISO consultant can help identify gaps and provide a remedy plan. You will also need to develop and implement measures to mitigate risks identified during the assessment.
Experts who have worked with enterprises like yours can help you comply with ISO 27001. They can also help you create security best practices to follow.
Step Four: Policy, Control Design, and Implementation
Now that you’ve recognized threats, determine how your organization will respond to them: which risks can you afford to ignore and which must you address?
Your auditor will analyze your ISO 27001 risk management process during your ISO 27001 certification assessment. As part of your audit evidence, you’ll need to provide a Statement of Applicability and a Risk Treatment Plan.
The Statement of Applicability indicates which ISO 27001 controls and policies apply to your company. A certification audit begins with an examination of this document. Reference control objectives from Annex A serve as a framework for evaluating the effectiveness of implemented controls and supporting your information security controls during compliance assessments.
A Risk Treatment Plan details how your company will deal with a threat identified in your risk assessment.
As per ISO 27001 standard outline, these are the steps:
-
Define risks
-
List all information assets
-
Check for weaknesses and threats
-
Evaluate risks
-
Lower risks by preventing their occurrence
-
Generate risk report
-
Review risk reports, make audits, and monitor perceived risks
After that, you’ll develop rules and procedures to address identified threats. Control implementation involves developing and executing security controls to address identified risks, including policy documentation, technical safeguards, and operational procedures. When designing controls, consider all relevant information security aspects to ensure comprehensive coverage. Implementing controls across departments is essential to ensure a strong and consistent security posture throughout the organization. Your policies should require multi-factor authentication and locked workstations when employees leave.
Step Five: Employee Training
Organizations must prioritize training employees on security policies and procedures as part of ISO 27001 requirements and information security best practices. This step ensures that everyone in your company understands data security and its role in achieving and maintaining compliance.
Employee training should cover data protection principles and legal requirements, such as those outlined in GDPR and ISO 27001, to ensure proper management of personal data and privacy risks.
It is also essential to educate staff on handling sensitive information, emphasizing confidentiality and security measures to maintain compliance and protect organizational data.
Step Six: Document and Collect Evidence
Obtaining your certification requires demonstrating that you have implemented the appropriate processes for an ISMS that complies with ISO 27001. Maintaining thorough documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance with information security management systems requirements.
You’ll need to provide your auditor proof that the company and its employees followed the procedures. In this list, you’ll find:
-
The Information Security Management System’s scope
-
Methods for evaluating and treating potential risks
-
Policy and ambitions for managing information security
-
Treatment Strategy for Potential Risks
-
Applicability Statement
-
The definition of security jobs and responsibilities
-
Risk evaluation and treatment report
-
Policy for limiting access
-
A list of all the things you own
-
Acceptable asset utilization
-
Security measures implemented by the supplier
-
IT management operating procedures
-
Principles of secure system engineering
-
Processes for ensuring business continuity
-
Procedure for handling incidents
-
Results are being monitored and measured
-
Compliance with all applicable laws, regulations, and agreements
-
Documentation of how the organization meets its compliance obligations under relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards
-
Records of education, training, work experience, and other credentials
-
The findings of a management review
-
The outcomes of the internal audit program
-
User activity logs, as well as exceptions and security incidents
-
Measures to remedy unsatisfactory performance
Step 7: Conduct an Audit for ISO 27001 Certification
Your organization must conduct an internal audit before submitting to an ISO audit by an external auditor. An internal audit comprises a thorough assessment of your company’s ISMS. It is one of the most effective methods to guarantee that your company’s ISMS runs successfully and complies with ISO 27001.
The next step is the initial certification audit, which consists of two stages of external audits conducted by an accredited certification body. In Stage 1, the accredited certification body will check your ISMS documents to ensure you have the appropriate policies and procedures. In Stage 2, the external auditors will examine your ISMS to ensure it satisfies ISO 27001 requirements by reviewing business processes and security measures. Choosing an accredited certification body is essential to ensure the validity and recognition of your ISO 27001 certification.
After Stages 1 and 2, you’ll receive a three-year ISO 27001 certification. If any nonconformities are identified during the audit, you must implement corrective actions to resolve them and maintain compliance.
Step Eight: Maintain Consistent Compliance
ISO 27001 emphasizes improvement. You must analyze and review your ISMS to ensure its effectiveness. As your firm grows and new vulnerabilities emerge, you’ll need to update processes and controls. As part of ongoing monitoring, ISO 27001 compliance requires internal audits. In addition, annual surveillance audits are mandatory yearly reviews conducted to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness of the information security management system. These audits typically involve documentation review and employee interviews and are essential for retaining certification. ISO 27001 is also part of a broader set of security management systems (ISMS) standards designed to help organizations manage information security risks. Before an external audit, internal auditors search for process and policy gaps and improvement possibilities.
Statement of Applicability
The Statement of Applicability (SoA) is a foundational document within the ISO 27001 certification process. It details the specific controls and procedures your organization has chosen to implement as part of its ISMS, based on the results of your risk assessment. The SoA outlines how your organization addresses information security risks and security risks, providing a clear rationale for each control’s inclusion or exclusion. It also describes the processes for risk assessment and risk treatment, ensuring that all identified risks are appropriately managed. The SoA serves as a key reference during the certification process, demonstrating your organization’s commitment to effective information security management and compliance with ISO 27001 requirements.
Incident Response
Incident response is a critical component of any effective information security management system, especially under ISO 27001. It involves a structured approach to detecting, reporting, and managing security incidents such as data breaches or cyber attacks. ISO 27001 requires organizations to develop and maintain an incident response plan that outlines procedures for containing and resolving security incidents, as well as for conducting post-incident reviews and implementing corrective actions. Regular internal audits and management reviews are essential to ensure that the incident response plan remains effective and up-to-date, enabling organizations to minimize the impact of security incidents and maintain compliance with ISO 27001.
Cost and Timeline for ISO 27001 Certification
As with a SOC 2 audit, the cost of attaining ISO 27001 certification depends on the number of employees and the organization's size since it affects the audit's duration. ISO 27001 certification expenses can range from $6–10K for small businesses to upwards of $25K for large enterprises.
Implementing an ISMS based on ISO 27001 might be a lengthy process involving numerous activities and individuals, depending on the organization's size. Structured approaches and well-defined scopes of work will help your firm implement ISO 27001 promptly and sustainably.
You must complete a full ISO 27001 audit every three years to maintain your accreditation. For your ISMS and deployed controls to continue to work effectively, ISO expects surveillance audits in years two and three. An external audit firm must conduct your organization's ISMS during those years. Once you establish your ISMS, you must maintain and improve it or risk compromising your ISO certification and blowing your surveillance audit.
ISO 27001 certification doesn't end information security management. It can develop and adapt with your organization, helping to keep your information secure as it evolves and potential challenges emerge.
ISO 27001 and CMMC Certification
If your organization participates in Department of Defense (DoD) contracts, you presumably know about the new Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) requirements, which will launch in 2025. The CMMC will substantially impact their ability to meet many companies' NIST 800-171 self-attestation requirements.
Here is a comparison between ISO 27001 and CMMC compliance.
Key Differences
The ISO and the IEC jointly developed the ISO/IEC 27000 series as an international standard for various organizations, not just the government sector. Therefore, there are government-specific needs in CMMC, but the ISO/IEC 27000 family does not have any of those criteria.
Commonalities
These guidelines include an organized security program, a codified risk assessment methodology, and customized information security controls. Given that such a significant portion of CMMC is derived from the NIST controls, there will inevitably be substantial overlap with the ISO/IEC 27000 family.
Should You Have Both Or Choose Between Them?
Many organizations find it best to pursue both, mainly because the ISO 27001 certification can serve as a basis for implementing essential CMMC components and best practices.
To fulfill the standards of the CMMC, you could require more resources, along with more tools and technology, and there will be a large amount of overlap between CMMC and ISO 27001. As a result, many businesses may find that making a parallel certification effort saves them both money and time. However, it takes significant planning on your part.
Differences Between CMMC, NIST, and ISO
With the CMMC standard, you ensure your firm is protected while working with government agencies and handling sensitive data. The NIST CSF and ISO/IEC 27001 standards cover non-sensitive data that any enterprise can use.
The NIST framework is more adaptable than CMMC and ISO standards because it has a highly segmented structure that makes it simple to learn, customize, and implement. This system focuses on voluntary compliance and self-certification, with no formal certification of conformity required.
Compared to ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST standards, CMMC is far more secure and stringent. Regarding data security, CMMC is unique in that it requires different security levels based on the sensitivity of the data a contractor is responsible for handling.
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard is a well-established security architecture that has gained widespread acceptance worldwide. NIST initially designed its framework to help U.S. agencies and businesses better manage risk. Similarly, the DoD established the CMMC framework to enhance the security of regulated data in the United States.
ISO 27001 emphasizes a risk-based management approach, while NIST CSF provides a more prescriptive, control-based structure. Additionally, ISO 27001 allows organizations to tailor controls to their specific risks, whereas NIST compliance generally requires implementing all specified controls.
Get the latest on the new NIS2 Directive.
Streamline Compliance with Automation
Even though these leading organizations primarily developed these security frameworks to protect various data, they share common security rules. You can determine the best framework for your business by the regulations that apply to it.
The good news is that by making adjustments and establishing methods for compliance with one framework, you'll also bring your firm closer to meeting numerous other cybersecurity criteria. Certification under ISO 27001 provides external verification of a strong security posture, which builds confidence with customers, partners, and investors, and offers a competitive advantage. Additionally, ISO 27001 certification enhances an organization's ability to meet regulatory and contractual obligations.
You need cybersecurity software that can scale with your compliance requirements and deliver automation at each level of cyber risk maturity. With CyberStrong, enterprises have access to any industry-recognized framework, including NIST 800-53, ISO 27001, CMMC, and custom frameworks unique to the organization. ISO 27001 certification can provide a competitive advantage by differentiating certified companies from non-certified competitors.
Leverage CyberSaint AI to automate assessments in just a few hours and crosswalk to one or many frameworks in just a few moments.
For more information on how CyberSaint can streamline your compliance, contact us.





.png)
.png)
.png)
%201.png)
.png)