For years, compliance has been one of the most resource-intensive responsibilities for cybersecurity teams. Despite growing investments in tools, the day-to-day reality of compliance is still dominated by manual, duplicative tasks. Teams chase down screenshots, review spreadsheets, and cross-check logs, often spending weeks gathering information before an assessment or audit.
This approach isn’t just inefficient; it also leaves organizations exposed. Manual processes increase the risk of errors, create audit delays, and limit visibility into the real-time effectiveness of security controls. In fact, research indicates compliance professionals allocate nearly 40% of their work hours to manual tasks, including evidence collection and reporting. It’s no wonder compliance has become known as a “tax” on security programs.
However, by 2026, automation will have fundamentally reshaped cybersecurity compliance. Forward-looking organizations are already investing in intelligent automation to remove the burden of low-value work, not to reduce headcount, but to empower their teams. Automation frees security professionals from tedious evidence hunts and control checks, allowing them to focus on higher-value activities, such as risk mitigation, resilience planning, and communicating with leadership in business terms.
Below are three of the most time-consuming compliance processes that organizations should automate by 2026, along with the tangible outcomes they can expect.
Three Compliance Processes to Automate
1. Automating Evidence Collection
The Challenge:
Manual evidence collection is a notorious time sink. Teams spend 20–40 hours per assessment gathering screenshots, downloading configs, and pulling PDFs across dozens of fragmented systems. For larger enterprises, the time commitment grows exponentially. Even API-based tools, while an improvement, fall short: they’re often limited by system permissions or data format restrictions, leaving gaps in the evidence needed for stringent audits.
The Solution:
Agentic AI and computer vision now enable the continuous capture and validation of evidence across all environments (cloud, on-premises, legacy systems, etc.) Unlike traditional approaches, this method doesn’t depend on narrow APIs. Evidence is continuously gathered, validated in real time, and mapped directly to compliance frameworks.
Why Automate:
- Comprehensive coverage: No gaps due to technical restrictions or outdated data.
- Always audit-ready: Auditors see a complete, validated evidence trail at any moment.
- Strategic focus: Compliance professionals stop acting as “evidence hunters” and start acting as risk advisors.
Expected Outcomes:
Organizations that automate evidence collection reduce time spent per audit cycle from weeks to hours, dramatically cut the risk of missing controls, and maintain continuous audit readiness rather than scrambling at the last minute.
How to Measure Improvements:
- Track hours spent on evidence collection before vs. after automation.
- Measure the percentage of controls validated automatically.
- Gather auditor feedback on the completeness and timeliness of evidence.
2. Automating Control Scoring and Monitoring
The Challenge:
Risk assessments are traditionally point-in-time and manual. Teams must gather logs, review evidence, and score controls, often in spreadsheets. This approach is slow, inconsistent, and quickly outdated. It’s no surprise that nearly 56% of businesses lack a unified view of risks across their infrastructure, making it almost impossible to understand real-time compliance posture.
The Solution:
Continuous Control Monitoring (CCM) leverages telemetry data from existing security tools, such as configuration scanners and monitoring systems, to automatically determine whether controls are operating as intended. Instead of reactive, labor-intensive reviews, organizations gain a live, dynamic view of compliance.
CCM automates how teams validate control effectiveness across evolving frameworks and risk conditions in real-time. No evidence chases, no manual control scoring, no more static snapshots.
Why Automate:
- Real-time visibility: Compliance posture updates are continuous, not just for the last quarter.
- Accuracy and consistency: Controls are scored uniformly across frameworks, eliminating human error.
- Empowered professionals: Teams can spend their time closing fundamental gaps instead of endlessly verifying controls.
Expected Outcomes:
Organizations that use automated control scoring experience faster reporting cycles, increased accuracy in compliance reporting, and scalability across complex frameworks such as NIST 800-53, ISO 27001, CIS Top 18, and PCI DSS 4.0.
How to Measure Improvements:
- Compare the number of controls automatically scored vs. manually scored.
- Track audit cycle times before and after automation.
- Monitor the reduction in rework or gaps flagged by auditors.
3. Automating Risk-to-Control Mapping and Correlation
The Challenge:
Manually correlating risks to threats and the controls that mitigate them is both time-consuming and error-prone. Security teams often rely on spreadsheets to map risks to MITRE ATT&CK tactics and controls, which can create blind spots and delay responses. Without automation, organizations struggle to prioritize effectively, leading to wasted effort on low-priority issues and slower reactions to critical threats.
The Solution:
Automating the mapping of risks to TTPs and controls enables organizations to dynamically connect threats, risks, and compliance requirements, thereby enhancing their ability to manage these elements effectively. This creates a living record that continuously updates as threats evolve, giving teams a clearer view of control effectiveness in a shifting landscape.
Why Automate:
- Faster insights: Reduce the time spent correlating risks, threats, and controls.
- Business alignment: Potential impact prioritizes risks, not just technical severity.
- Strategic empowerment: Teams focus on proactive defense and communication, not clerical correlation tasks.
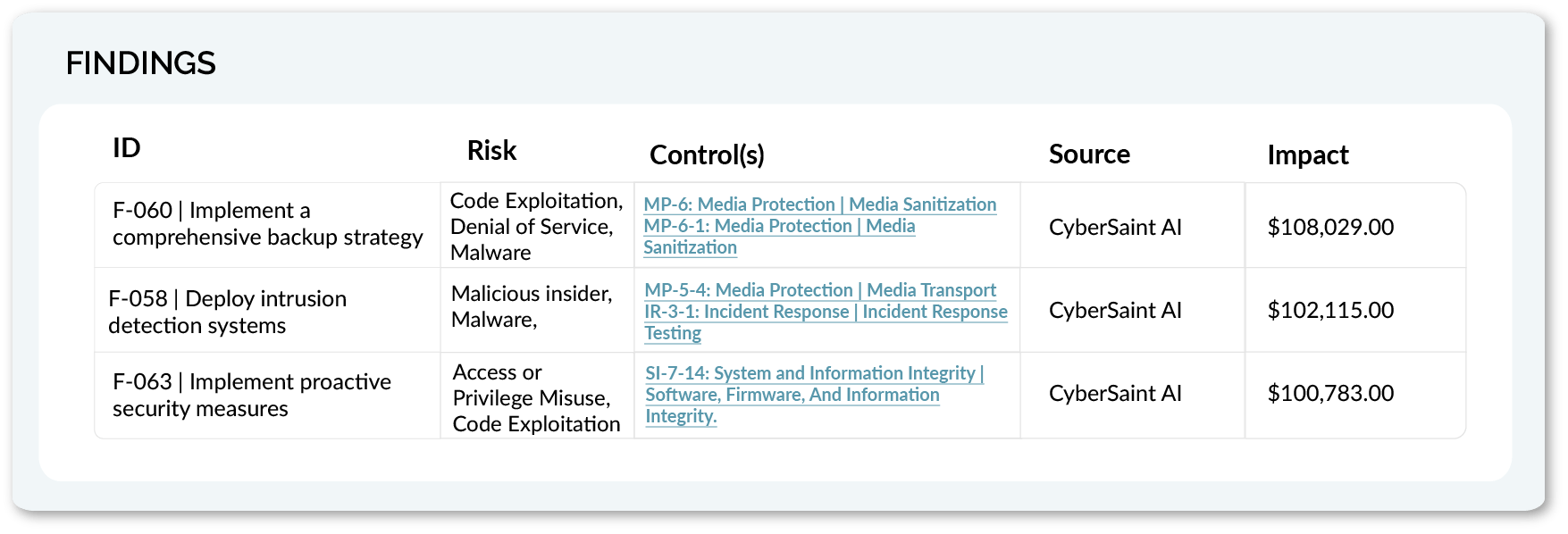
Expected Outcomes:
Organizations gain accurate automated risk assessments, reduced response times, and a stronger link between day-to-day security operations and compliance reporting.
How to Measure Improvements:
- Track the time required to map new risks before and after automation.
- Measure the number of high-risk threats prioritized automatically.
- Monitor improvements in incident response, such as reductions in mean time to respond (MTTR).
Challenges in Transitioning from Manual to Automated Compliance
Switching from manual to automated compliance is a transformative shift, and like any change, it comes with hurdles:
- Change management: Moving from spreadsheets to AI-driven workflows requires cultural buy-in. Teams must learn to trust and embrace new processes.
- System integration: The initial setup requires effort, particularly when connecting legacy systems.
- Trust building: Teams may need time to validate automated outputs before entirely relying on them. Hybrid workflows, where automation handles heavy lifting and humans provide oversight, can help ease this transition.
The key is to understand automation as a tool for empowerment. It doesn’t replace skilled professionals, it ensures their time is spent where it creates the most value: mitigating risk, improving resilience, and strengthening the organization’s security posture.
Preparing Automated Cybersecurity Compliance for 2026
By 2026, organizations that thrive will stop wasting time on manual compliance work. Evidence collection, control scoring, and AI-powered control mapping are three areas that can and should be automated.
Automation doesn’t diminish the role of compliance and security teams. Instead, it elevates it. By removing the manual, duplicative work, automation frees professionals to do what they do best: think strategically, act decisively, and safeguard the enterprise in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
CyberStrong is already leading this shift, delivering real-time, audit-ready compliance and continuous risk visibility at enterprise scale. For security and compliance professionals, automation is more than efficiency; it’s the path to proving control effectiveness, reducing risk, and securing the future of compliance.





.png)
.png)
.png)
%201.png)
.png)